The film “Kiss the Ground” has put the importance of soil health back on the agenda. A quick round-up for those of you who haven´t watched it: The movie draws an optimistic picture that the soil’s ability to sequester carbon could help to mitigate the effects of climate change. After watching, I asked myself: Is soil the only hope we have, to tackle an upcoming crisis? So I want to dive into the vital role of soil in this blog post with you.
The Composition of Soil
To understand the vital role soil has within an ecosystem, we should look at its composition first. When you use a shovel to dig out soil from a garden, what do you observe? According to National Geographic, the soil consists of a mixture of abiotic and biotic factors. 1
Abiotic factors are non-living elements, of an ecosystem. For instance, sun, water, or air are abiotic factors, that influence the growth of trees. In the ground, the abiotic factors, include water, minerals, and air. Common minerals in the soil are phosphorus, potassium, and nitrogen gas. They support plant growth. 1 2
Biotic factors, on the other hand, are living organisms within an ecosystem. We are talking about a range from small bacteria to big mammals. All of them fulfil a unique role to maintain an ecosystem´s functioning. Biotic components of the soil include a range of living organisms such as plants and animals for example worms, fungi, or microorganisms. The soil itself has great biodiversity! According to Dr. Kristine Nicholas, chief scientist from Rodale institute, healthy soil contains more organisms in a single handful than the total number of people who have ever lived on Earth. “Kiss the Ground” highlights that important soil organisms for carbon sequestration are microbes. 1 3 4
Microbes: A Key Solution for Climate Change?
What exactly is carbon sequestration, and how does it work? Carbon sequestration is the storage of atmospheric Carbon in a carbon pool. 5 This carbon pool can be within plants or the soil. The film demonstrates that soil can capture far more carbon than the atmosphere and plants combined. As a result, the soil may play a vital role in combating climate change. 4 But how does the soil sequester carbon, and what role do microbes play?
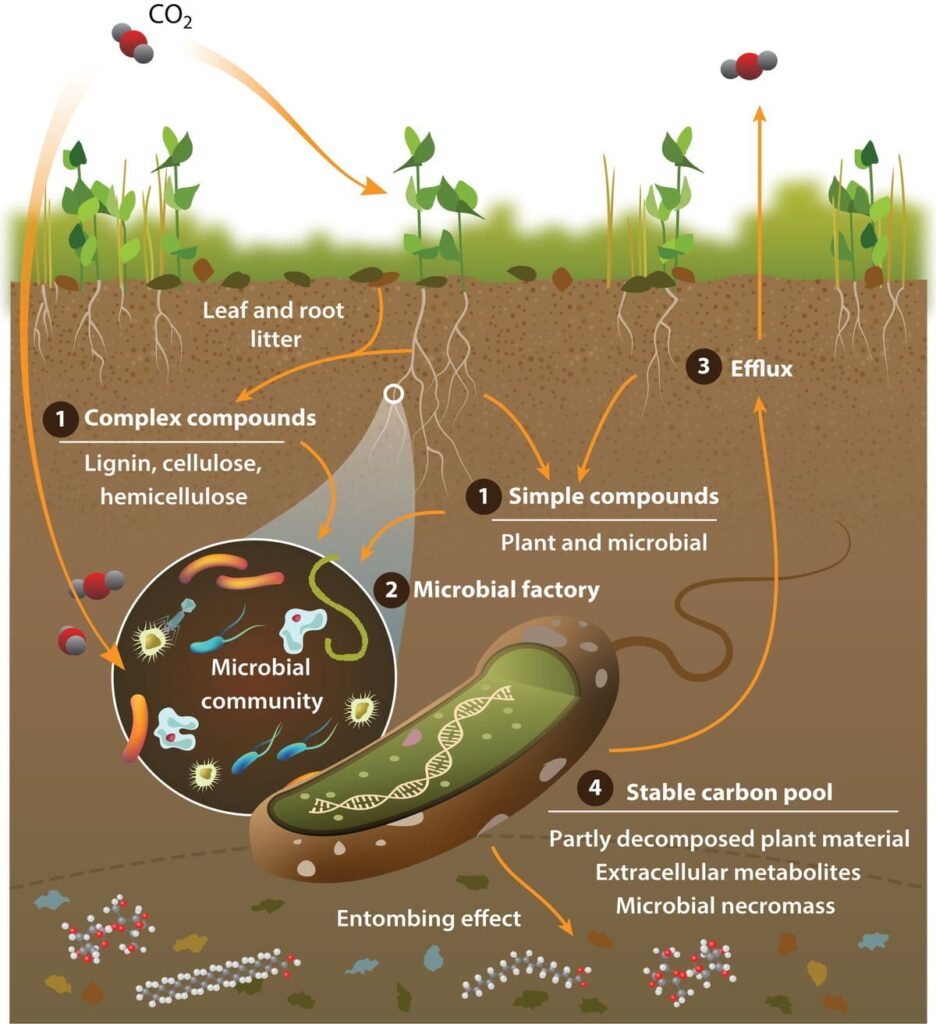
Soil carbon cycle through the microbial loop (altered after Wikimedia Commons, s.a.)
Nutrient cycling in the soil
Soil microbes play a significant role in nutrient cycling. Plants fixate CO2 from the atmosphere during photosynthesis. This carbon enters the soil through the plant’s roots. It can, however, come from fallen leaves or litter as well. The microbial community decomposes plant material and stores it in a stable carbon pool.
The soil microbes play a vital role in making nutrients available for the plant. The plant returns the favour by supplying the microbes with carbon. 4 This process is a component of the carbon cycle. This is a beautiful example of how evolution has perfectly coordinated natural processes, in my opinion.
How soil provides essential ecosystem services
The soil provides other ecosystem services in addition to carbon sequestration and nutrient cycling.. Healthy soil is important for water retention. In other words, as land deteriorates, it loses its ability to retain water, which can lead to flooding during periods of heavy rainfall. This is a major problem that goes hand in hand with soil erosion. Soil erosion is caused by the overuse of land in the form of agricultural tilling practices and pesticide contamination of the soil. Pesticides are destroying the microbial community. And you already know that microbes are essential for soil health. Further, the soil loses its fertility as a result of erosion and thus can no longer supply the local population. That´s why sustainable agriculture and soil management are so important. 4
Conclusion
In summary, the film “Kiss the Ground” reminds us of the incredible power of soil and the critical role it plays in sustaining life on our planet. With its ability to sequester carbon and provide important ecosystem services like water retention and nutrient cycling, healthy soil has the potential to be a key ally in the fight against climate change and food insecurity. I recommend watching the movie yourself to get an impression of how strong the impact of sustainable agriculture can be.
References:- National Geographic, s.a. Soil Composition. Available at: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/soil-composition/ [Accessed on 05.03.2023].
- National Geographic, s.a. Abiotic Factors. Available at: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/resource-library-abiotic-factor/ [Accessed on 05.03.2023].
- National Geographic, s.a. Biotic Factors. Available at: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/resource-library-biotic-factors/ [Accessed on 05.03.2023].
- Roth, J., Tickell, J., & Hawken, P., 2020. Kiss the Ground. United States.
- Bhattacharyya, S.S., Ros, G.H., Furtak, K., Iqbal, H. M.N. and Parra-Saldívar, R., 2022. Soil carbon sequestration – An interplay between soil microbial community and soil organic matter dynamics. Science of The Total Environment. Volume 815. p.152928-152928.

 To provide scientific knowledge on this site for free means a lot to me. However, researching and writing costs me a lot of time. Since I´m a student, financial support for my blog post helps me to maintain scientific quality.
To provide scientific knowledge on this site for free means a lot to me. However, researching and writing costs me a lot of time. Since I´m a student, financial support for my blog post helps me to maintain scientific quality.